Electric Vehicle 101
|
An electric vehicle (EV) is any vehicle that is powered by a battery that has been charged by an external electricity source. Electric vehicles have been in existence as long as gasoline-powered cars, but have often been more expensive than conventional gas powered cars.
Today, concerns about rising greenhouse gas emissions and a desire to save money at the gas pump have led more manufacturers to focus on fuel efficiency and electric vehicle technology. Since the early 2000s, almost all major vehicle manufacturers released or plan to release an electric or hybrid vehicle. There are two different types of EVs that you’ll see on the road today: battery electric vehicles (BEVs) and plug-in hybrid electric vehicles (PHEVs). Hybrid electric vehicles (HEVs) are technically EVs. However, they do not require a plug-in charge. |
If you're curious about electric vehicle charging, visit our EV Charging 101 page.
|
Image: Drive Electric Tennessee, Electric Vehicle 101.
May 2020. http://driveelectrictn.org/about-evs/ |
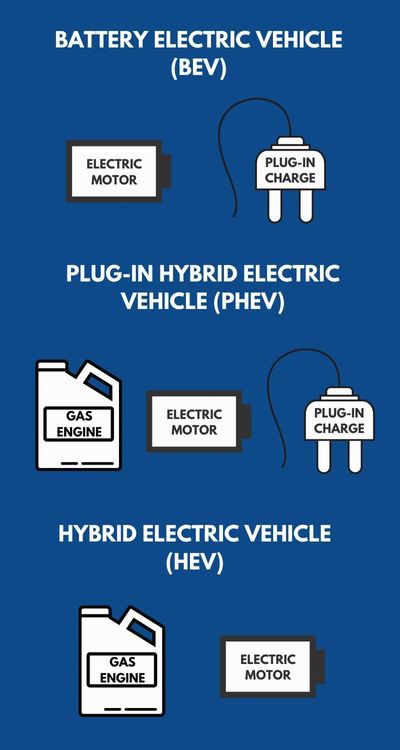
Types of Electric VehiclesElectric vehicles are available in three models: battery electric vehicles (BEV), plug-in hybrid electric vehicles (PHEVs), and hybrid electric vehicles (HEVs). PHEVs and HEVs use electricity to improve fuel efficiency whereas EVs have no traditional fuel tank and therefore are the least polluting vehicle available in the world right now. Both light-duty and heavy-duty electric vehicles are now available in the marketplace!
Battery Electric Vehicles (BEVs)
Battery electric vehicles (BEV) use an electric motor and battery instead of a conventional gas tank and internal combustion engine. Also referred to as all-electric vehicles, plug-in vehicles (PEV), or simply electric vehicles, BEVs use a battery pack to store electrical energy that powers the motors. BEVs are charged by plugging the vehicles into an electric power source and are considered zero-emission vehicles because they produce no direct exhaust or emissions. Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicles (PHEVs)
Plug-in hybrid electric vehicles (PHEVs) use batteries to power an electric motor AND a gas-powered internal combustion engine. PHEVs operate using batteries and an electric motor until the battery energy is nearly depleted, switching over to the internal combustion engine to provide power. Similarly to BEVs, PHEVs can be plugged into electrical sources to charge on-board batteries. PHEVs are also fueled like internal combustion engines. Because of the small on-board battery, it’s possible to drive moderate distances just using electricity and produce lower levels of emissions with each trip. Hybrid Electric Vehicles (HEVs)
Hybrid electric vehicles (HEVs) are powered by an internal combustion engine with one or more electric motors that use energy stored in batteries. HEVs can have a substantial range on a single tank of gas, but are not required to be plugged-in for charging and still require conventional petroleum based fuel. HEVs may use the extra power provided by the electric motor to allow for a smaller engine. The battery can also power auxiliary loads and reduce engine idling when the vehicle is stopped. HEVs use regenerative braking to capture energy normally lost during braking by using the electric motor as a generator and storing the captured energy in the battery. |
Top 10 Models in
|
|
Other Models to Consider
Light-, medium-, and heavy-duty EVs are commercially available and new models are appearing every year. EVs can also save you money through fuel savings, available tax credits, and other New York State opportunities. Keep scrolling for a 2024 list of available light-duty electric vehicle models.
BEV Examples4-Door Sedan/Wagon
2-Door Hatchbacks
SUVs
|
PHEV ExamplesSUVs
Vans/Pickups
|
HEV Examples4-Door Sedans/Wagons
SUVs
Vans/Pickups
|
See a vehicle you like? Visit PlugStar, Con Edison or the Alternative Fuels Data Center for more information on vehicle specs, cost comparisons, charging time, & more!
|
Shopping Assistant
PlugStar's shopping assistant makes it easy to estimate incentives, costs and environmental footprint for specific EV models. |
Vehicle Calculator
Find a specific model or browse by category and easily compare your favorite car models based on fuel efficiency, available incentives and total cost of ownership. |
AFDC Vehicle Cost Calculator
Compare cost of ownership and emissions for most vehicle models. |
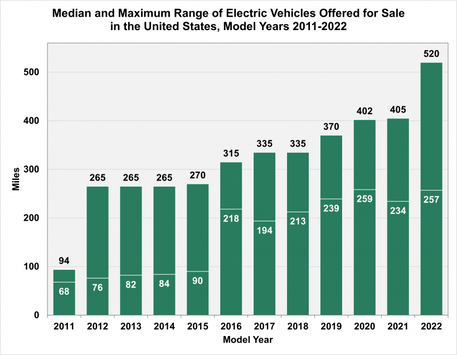
Driving Range
|
"Note: Range is based on Environmental Protection Agency estimates. Does not include plug-in hybrid vehicles. Source: U.S. Department of Energy and U.S. Environmental Protection Agency
|
In 2022, electric vehicles (EVs) have come a long way. They now have a median driving range of 257 miles per charge, based on data from the U.S. Department of Energy Fuel Economy Guide. Many EV models can even go beyond 300 miles on a single charge. However, it's important to know that the range of EVs can change depending on different factors. Extreme temperatures, high speeds, rapid acceleration, heavy loads, and steep inclines all affect how far an EV can go on a charge because they use more energy. Despite these challenges, the EV market is growing, thanks to more powerful models and commitments from automakers to make more electric vehicles. |
How much can I save with an EV?Electric vehicles require less maintenance than internal combustion engine vehicles and have lower fuel costs when considering the price of electricity versus gas or diesel. When you account for financial incentives, electric vehicles become much more affordable and competitive with gas vehicles.
There's never been a better time to buy an electric vehicle! As a New York State resident, you can save up to $9,500 on a new electric vehicle lease or purchase.
|